2021/04/06
Part 6: Electric Linear Actuators With Feedback Sensors
Noticias/eventos
|
Contents |
|
2. Summary: Advantages and Disadvantages of Feedback Sensors |
It is always essential to be informed about the basics and factors leading up to selecting a product before committing to the specific model for your needs. TiMOTION is a vertically integrated, electric linear actuator and control system manufacturer with the ability to customize products to meet your specifications. Previous articles have explained the essential components and functions of an electric linear actuator; the optional safety features TiMOTION offers, the load and speed characteristics, and IP ratings and lubrication. This whitepaper highlights a critical discussion regarding the four main position feedback sensors used within TiMOTION’s linear motion systems.
When an electric linear actuator is equipped with feedback sensors, the actuator can actively communicate its stroke position to the control system (sometimes referred to as positioning). These output sensors also allow for the control box to precisely regulate the actuator’s stroke at all times. While this is not required on all linear actuators, positional sensors are required on those with more complex functionality. For example, if an actuator needs to move synchronously with another, feedback sensors are necessary to monitor and ensure both linear actuators remain in sync, regardless of differences in load. Additionally, feedback sensors are crucial for memory positioning and other special features that require knowing where the actuator’s stroke position is at all times. This can include but is not limited to, motor speed, conditional movement, and other features.
The Four Main Position Feedback Sensors That TiMOTION Uses Within Our Linear Actuators Are:
1. Hall Effect Sensors
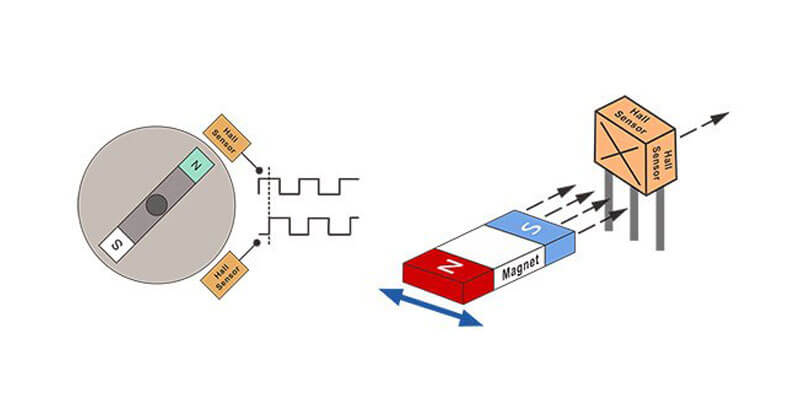
Hall Effect sensors are TiMOTION’s most recommended type of positional sensors for electric actuators because they are small enough to fit in compact spaces, providing higher resolution and digital output for positioning and synchronization. NOTE: TiMOTION’s control systems are designed to integrate with HALL sensors only. Our control systems will not register feedback from any other type of sensor.
These Hall Effect sensors are activated by a magnetic field, comprised of two important characteristics: flux density and polarity. The output signal from a Hall Effect sensor is the magnetic field density function around the device. When the magnetic field density around the sensor exceeds a certain pre-determined threshold, the sensor detects it and generates an output voltage called the Hall Voltage, or VH.
Hall sensors are commonly used due to their cost-efficiency. These sensors also maintain their quality over time and generally have long lifespans.
MA2 |
TA16 |
 |
 |
2. Potentiometers
Potentiometers, also known as POT sensors, are generally the most commonly used output sensor in the industrial marketplace. They have a wiper contact linked to a mechanical shaft that can either be rotational or linear in their movement. This causes the resistance value between the wiper and the two end connections to change, giving an electrical signal output proportional to the actual wiper position on the resistive track and its resistance value.
In other words, resistance determines position. As the linear actuator leads screw turns, the resistance value between the wiper and the two end connections will change. Each resistance value will correspond with the position of the linear actuator’s stroke.
One advantage of the POT sensor versus a Hall sensor is that when the power is off, the POT will keep the position's information, while a Hall sensor will lose the positional information and need to be reset. However, potentiometers are slightly less accurate in their readings than the Hall Effect sensor due to the initial installation process. Yet, this is not detrimental to the overall position reading.
MA1 |
TA29AC |
 |
 |
3. Reed Sensors
Reed sensors are magnetic feedback sensors. An applied magnetic field operates an electrical switch, and the sensor as a whole contains a pair of contacts on ferrous metal reeds in a hermetically sealed glass envelope. The contacts may be normally open, closing when a magnetic field is present, or vice versa. The switch may be actuated by a coil, making the reed switch return to its original position. With force from each rotation of the lead screw and position of the linear actuator stroke length, the reed switch will open or close. TiMOTION specifically uses its Reed sensors inside the handsets with a safety key function to send a signal when the key has been removed or uses Reed sensors to adjust the end of the stoke.
MA2 |
TA2P |
 |
 |
4. Optical Sensors
Optical sensors are also occasionally used in TiMOTION’s electric actuators. An optical sensor functions by converting light into an electronic signal. As a lead screw rotates, a light-blocking wheel will also rotate at the same time, blocking the light to the optical coupler. This optical coupler will send a signal each time it senses the light being blocked. The light-blocking wheel revolutions will cause the optical coupler to send twenty-five signals each full revolution.
Summary: Advantages and Disadvantages of Feedback Sensors
|
Sensor Type |
Hall Sensors |
Potentiometer |
Reed Sensors |
|
Main Features |
The Hall-effect sensor makes it possible to count the motor revolutions by using magnets fixed on the motor shaft. A microprocessor counts the revolutions. |
The potentiometer consists of a slider sliding on a resistor whose role is to measure the value of this resistor. Each value of resistance corresponds to the position of the actuator stroke. |
The reed sensor is a magnetic position sensor. It is an electrical switch activated by the application of a magnetic field. It consists of two contacts mounted on ferrous metal strips contained in a sealed glass enclosure. The contacts are normally open or closed. |
|
Advantages |
|
|
|
|
Disadvantages |
|
|
|
Overall, the process of choosing the right electric linear actuation system for your application is one that you must carefully research before purchasing. TiMOTION is proud to offer many customization options in addition to knowledgeable customer service to help you create the perfect solution.










